Bearing is the most important element in the day to day life applications. As a mechanical engineer or Mechanical design Engineer you must know how Bearing selection is done. From this article you will learn that Bearing selection procedure, Bearing selection calculations, How to select bearing from manufacturers catalogue, What are the top companies of all bearing, types of bearings.
Highlights
1.BASICS
2. TYPES OF ROLLING CONTACT BEARINGS
3. SELECTION OF BEARING-TYPE
4.STATIC, DYNAMIC AND EQUIVALENT LOAD CARRYING CAPACITY
5. LIFE OF BEARING FOR VARIOUS APPLICATIONS
6. DESIGNATION OF ROLLING CONTACT BEARING
7. SELECTION OF BEARING FROM MANUFACTURER’S CATALOGUE
8. APPLICATIONS OF SLIDING CONTACT BEARING AND ROLLING CONTACT BEARING
9. LUBRICATION OF BALL AND ROLLER BEARINGS
10. MOUNTING OF BEARING
11. BEARING MATERIALS
12. BEARING COMPANIES
13. BASIC QUESTIONS ASKED IN INTERVIEW
1. Basics:
Bearing is a mechanical element that permits relative motion between two parts, such as the shaft and the housing, with minimum friction.
The functions of the bearings are as follows.
1.The bearing ensures free rotation of the shaft or the axle with minimum friction.
2.Bearing supports the shaft or the axle and holds it in the correct position.
3.It takes up the forces that act on the shaft or the axle and transmits them to the frame or the foundation.
Classification of bearings
- Depending on load applied
-
- Radial bearing- Which takes load perpendicular to shaft.
- Thrust bearing- Which takes axial load.
- Depending upon type of friction.
-
- Sliding contact bearing.
- Rolling contact bearing.
2. TYPES OF ROLLING CONTACT BEARINGS:
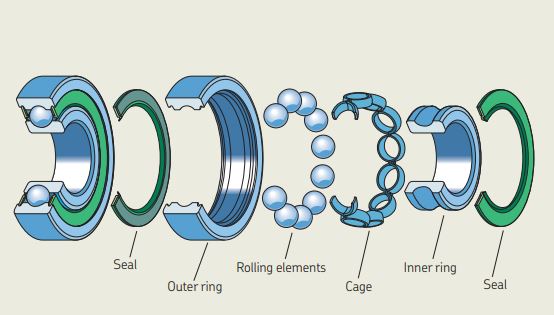
A rolling contact bearing consists of four parts inner and outer races, a rolling element like ball, roller or needle and a cage which holds the rolling elements together and spaces them evenly around the periphery of the shaft.
Depending upon the type of rolling element, the bearings are classified as ball bearing, cylindrical roller bearing, taper roller bearing and needle bearing.
1.Deep Groove Ball Bearing:
The most frequently used bearing is the deep groove ball bearing. found in almost all kinds of products in general mechanical engineering.
Deep groove ball bearing has the following advantages:
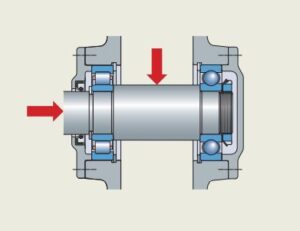
(a) Due to relatively large size of the balls, deep groove ball bearing has high load carrying capacity.
(b) Deep groove ball bearing takes loads in the radial as well as axial direction.
(c) Due to point contact between the balls and races, frictional loss and the resultant temperature rise is less in this bearing. The maximum permissible speed of the shaft depends upon the temperature rise of the bearing. Therefore, deep groove ball bearing gives excellent performance, especially in high-speed applications.
(d) Deep groove ball bearing generates less noise due to point contact. (e) Deep groove ball bearings are available with bore diameters from a few millimetres to 400 millimetres.
2.Cylindrical Roller Bearing:
When maximum load carrying capacity is required in a given space, the point contact in ball bearing is replaced by the line contact of roller bearing. A cylindrical roller bearing consists of relatively short rollers that are positioned and guided by the cage.
Cylindrical roller bearing offers the following advantages:
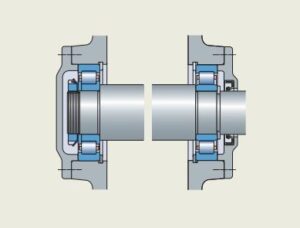
(a) Due to line contact between rollers and races, the radial load carrying capacity of the cylindrical roller bearing is very high.
(b) Cylindrical roller bearing is more rigid than ball bearing.
(c) The coefficient of friction is low and frictional loss is less in high-speed applications.
3.Angular Contact Bearing:
In angular contact bearing, the grooves in inner and outer races are so shaped that the line of reaction at the contact between balls and races makes an angle with the axis of the bearing. This reaction has two components— radial and axial.
Therefore, angular contact bearing can take radial and thrust loads. It is often used in pairs, either side by side or at the opposite ends of the shaft, in order to take the thrust load in both directions.

Angular contact bearings offer the following advantages:
(a) Angular contact bearing can take both radial and thrust loads.
(b) In angular contact bearing, one side of the groove in the outer race is cut away to permit the insertion of larger number of balls than that of deep groove ball bearing. This permits the bearing to carry relatively large axial and radial loads. Therefore, the load carrying capacity of angular contact bearing is more than that of deep groove ball bearing.
4.Self-aligning Bearings:
There are two types of self-aligning rolling contact bearings, viz., self aligning ball bearing and spherical roller bearing. The principle of self-aligning bearing is explained in the next section.
The self-aligning ball bearing consists of two rows of balls, which roll on a common spherical surface in the outer race. In this case, the assembly of the shaft, the inner race and the balls with cage can freely roll and adjust itself to the angular misalignment of the shaft.
5.Taper Roller Bearing:
The taper roller bearing consists of rolling elements in the form of a frustum of cone. They are arranged in such a way that the axes of individual rolling elements intersect in a common apex point on the axis of the bearing.
In kinematics’ analysis, this is the essential requirement for pure rolling motion between conical surfaces. In taper roller bearing, the line of resultant reaction through the rolling elements makes an angle with the axis of the bearing.
Taper roller bearings offer the following advantages:

(a) Taper roller bearing can take heavy radial and thrust loads.
(b) Taper roller bearing has more rigidity.
(c) Taper roller bearing can be easily assembled and disassembled due to separable parts.
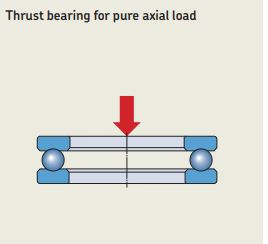
6.Thrust Ball Bearing:
A thrust ball bearing consists of a row of balls running between two rings—the shaft ring and the housing ring. Thrust ball bearing carries thrust load in only one direction and cannot carry any radial load. The use of a large number of balls results in high thrust load carrying capacity in smaller space.
3. SELECTION OF BEARING-TYPE
(i)For low and medium radial loads, ball bearings are used, whereas for heavy loads and large shaft diameters, roller bearings are selected.
(ii) Self-aligning ball bearings and spherical roller bearings are used in applications where a misalignment between the axes of the shaft and housing is likely to exist.
(iii) Thrust ball bearings are used for medium thrust loads whereas for heavy thrust loads, cylindrical roller thrust bearings are recommended. Double acting thrust bearings can carry the thrust load in either direction.
(iv) Deep groove ball bearings, angular contact bearings and spherical roller bearings are suitable in applications where the load acting on the bearing consists of two components— radial and thrust.
(v) The maximum permissible speed of the shaft depends upon the temperature rise in the bearing. For high-speed applications, deep groove ball bearings, angular contact bearings and cylindrical roller bearings are recommended.
(vi) Rigidity controls the selection of bearings in certain applications like machine tool spindles. Double row cylindrical roller bearings or taper roller bearings are used under these conditions. The line of contact in these bearings, as compared with the point of contact in ball bearings, improves the rigidity of the system.
(vii) Noise becomes the criterion of selection in applications like household appliances. For such applications, deep groove ball bearings are recommended.
4. STATIC LOAD CARRYING CAPACITY:
Static load is defined as the load acting on the bearing when the shaft is stationary. It produces permanent deformation in balls and races, which increases with increasing load. The permissible static load, therefore, depends upon the permissible magnitude of permanent deformation
5. DYNAMIC LOAD CARRYING CAPACITY:
The dynamic load carrying capacity of a bearing is defined as the radial load in radial bearings (or thrust load in thrust bearings) that can be carried for a minimum life of one million revolutions.
6. EQUIVALENT BEARING LOAD:
The equivalent dynamic load is defined as the constant radial load in radial bearings (or thrust load in thrust bearings), which if applied to the bearing would give same life as that which the bearing will attain under actual condition of forces.
The expression for the equivalent dynamic load is written as,
P = XVFr + YFa
where,
P = equivalent dynamic load (N)
Fr = radial load (N)
Fa = axial or thrust load (N)
V = race-rotation factor

X and Y are radial and thrust factors respectively and their values are given in the table. The race-rotation factor depends upon whether the inner race is rotating or the outer race. The value of V is 1 when the inner race rotates while the outer race is held stationary in the housing.
The value of V is 1.2 when the outer race rotates with respect to the load, while the inner race remains stationary. In most of the applications, the inner race rotates and the outer race is fixed in the housing. Assuming V as unity, the general equation for equivalent dynamic load is given by,
P = XFr + YFa,
we will use the above equation for calculating equivalent dynamic load. The effect of V should be considered in special cases, where the outer race rotates and the inner race is stationary. When the bearing is subjected to pure radial load Fr , P = Fr
When the bearing is subjected to pure thrust load Fa , P = Fa
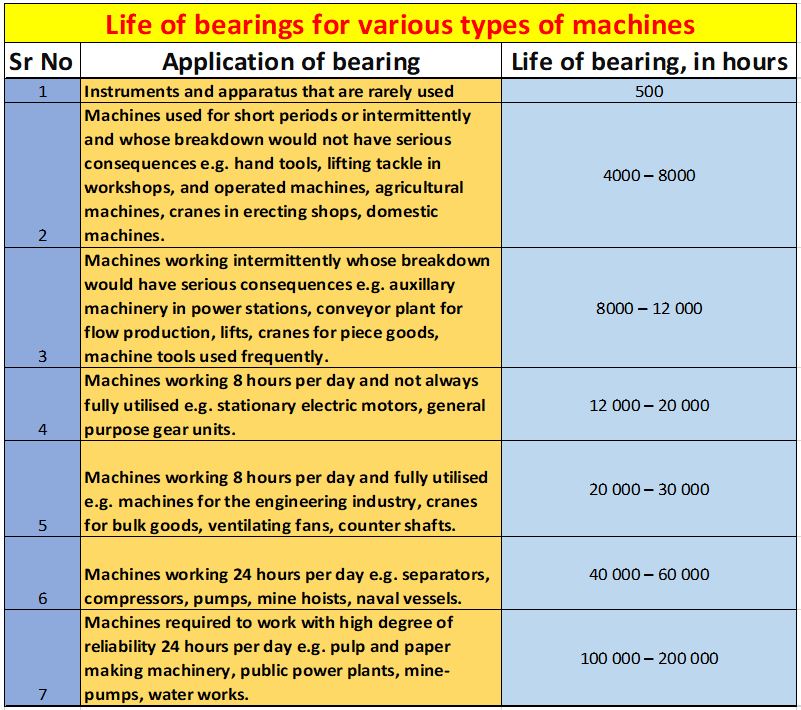
7. LIFE OF BEARING FOR VARIOUS APPLICATIONS:
While bearing selection life of bearing is one of the important factor.
Life of bearing is expressed in terms of hours or millions of revolutions.
In application like vehicle the speed of rotation is not constant and desired bearing life is expressed in terms of millions of revolutions.
In other applications speed is relatively constant and desired life is expressed in terms of hours of service.
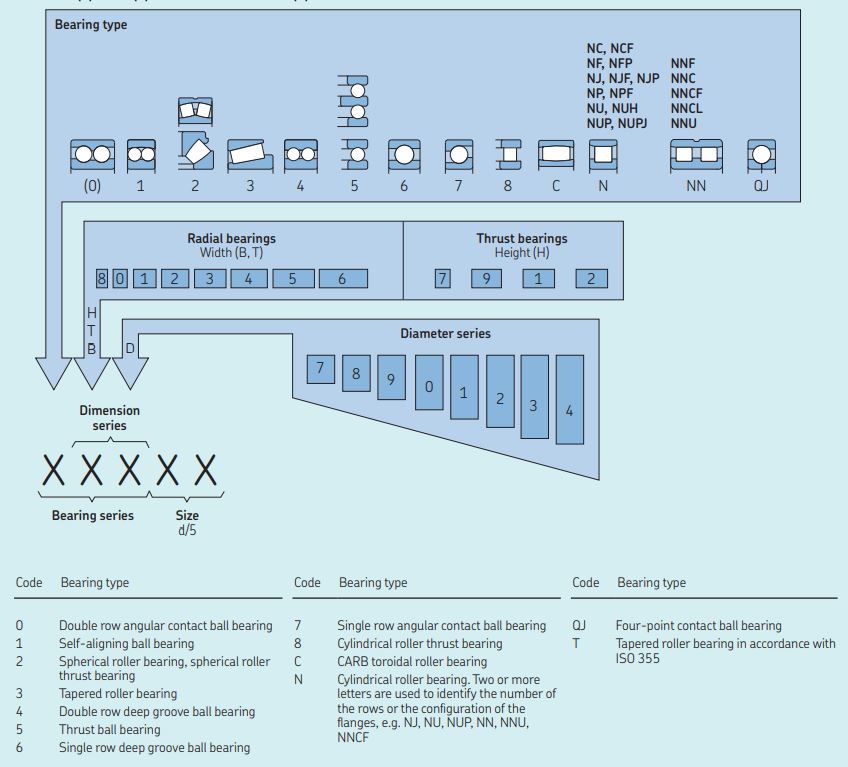
8. DESIGNATION OF ROLLING CONTACT BEARING:
A rolling contact bearing is usually designated by three or four digits. The meaning of these digits is as follows:
- The last two digits indicate the bore diameter of the bearing in mm (bore diameter divided by 5). For example, XX05 indicates a bearing of 25 mm bore diameter.
- The third digit from the right indicates the series of the bearing. The numbers used to indicate the series are as follows:
Extra light series –1
Light series – 2
Medium series – 3
Heavy series – 4
For example, X307 indicates a medium series bearing with a bore diameter of 35 mm.
- The fourth digit and sometimes fifth digit from the right specifies the type of rolling contact bearing.
- For example, the digit 6 indicates deep groove ball bearings
- If the bearing series starts with code,
0 – Double row angular contact ball bearing.
1 – Self-aligning ball bearing.
2 – Spherical roller bearing, spherical roller thrust bearing.
3 – Tapered roller bearing.
4 – Double row deep groove ball bearing.
5 – Thrust ball bearing.
6 – Single row deep groove ball bearing.
7 – Single row angular contact ball bearing.
8 – Cylindrical roller thrust bearing.
9. SELECTION OF BEARING FROM MANUFACTURER’S CATALOGUE:
Step 1: Calculate the axial and radial forces acting on the bearing and determine the shaft diameter of the shaft where the bearing is to be fitted.
2: Select type of bearing according to application.
3: Determine the values of radial(X) and thrust (Y) factors from catalogue. The values depend upon two ratios, (Fa/Fr) and (Fa/Co)
Where, Co is the static load capacity.
Step 4: Calculate the equivalent dynamic load from the equation.
P = XFr + YFa
Step 5: Make a decision about the expected bearing life and express the life L10 in million revolutions.
Step 6: Calculate the dynamic load capacity from the equation,
C = P ( L10) 1/3
Step 7: Check whether the selected bearing of series 60 has the required dynamic capacity. If not, select the bearing of the next series and go back to Step (iii) and continue.
10. APPLICATIONS OF SLIDING CONTACT AND ROLLING CONTACT BEARING:
Bearing selection is basically based on application.
Sliding contact Bearing
- Crankshaft bearings in petrol and diesel engines;
- Centrifugal pumps;
- Large size electric motors;
- Steam and gas turbines;
- Concrete mixers, rope conveyors and marine installations.
Rolling contact Bearing:
- Machine tool spindles;
- automobile front and rear axles;
- gear boxes;
- small size electric motors;
- rope sheaves, crane hooks and hoisting drums.
11. LUBRICATION OF BALL AND ROLLER BEARINGS:
- Reduce friction and wear between the sliding parts of the bearing,
- Prevent rusting or corrosion of the bearing surfaces,
- To protect the bearing surfaces from water, dirt etc.,
- Dissipate the heat.
12. MOUNTING OF BEARING:
- Mounting should be carried out in a dust free and dry environment. Machines which produce metal particles, chips or sawdust should not be located in the vicinity of the mounting operation.
- Before assembly, the shaft and the housing bore should be inspected. The burrs on the shaft and the shoulders should be removed. The accuracy of the form and dimensions of the shaft and bearing seat in the housing should be inspected.
- The bearing should not be taken out from its package until before it is assembled. The rust-inhibiting compound on the bearing should not be wiped except on the outer diameter and bore surface. These inner and outer surfaces are cleaned with white spirit and wiped with clean cloth.
- Small bearings are mounted on the shaft with the help of a small piece of tube or ring. Blows are applied by means of a hammer on this tube or ring. Direct blows should never be applied to the bearing surface, otherwise the race or the cage may get damaged. The tube or the metallic ring is placed against the inner race and the blows are applied with an ordinary hammer all around the periphery of the ring.
- Medium size bearings are mounted on the shaft by pressing the tube or the metallic ring by means of a hydraulic or mechanical press. Large size bearing is mounted by heating it to 80° to 90°C above the ambient temperature by induction heating and then shrinking it on the shaft. The bearing should never be heated by direct flame.
13. BEARING MATERIALS:
Required desired bearing properties while bearing selection:
- When metal to metal contact occurs, the bearing material should not damage the surface of the journal. It should not stick or weld to the journal surface.
- It should have high compressive strength to withstand high pressures without distortion.
- In certain applications like connecting rods or crankshafts, bearings are subjected to fluctuating stresses. The bearing material, in these applications, should have sufficient endurance strength to avoid failure due to pitting.
- The bearing material should have the ability to yield and adopt its shape to that of the journal. This property is called conform-ability. When the load is applied, the journal is deflected resulting in contact at the edges. A conformable material adjusts its shape under these circumstances.
- The dirt particles in lubricating oil tend to jam in the clearance space and, if hard, may cut scratches on the surfaces of the journal and bearing. The bearing material should be soft to allow these particles to get embedded in the lining and avoid further trouble. This property of the bearing material is called embeddability.
- In applications like engine bearings, the excessive temperature causes oxidation of lubricating oils and forms corrosive acids. The bearing material should have sufficient corrosion resistance under these conditions.
- The bearing material should have reasonable cost and should be easily available in the market.
The most popular bearing material is Babbitt. Due to its silvery appearance, Babbitt is called ‘white’ metal. There are two varieties of Babbitt lead-base and tin-base, depending upon the major alloying element. They are used in the form of a strip or thin lining about 0.5 mm thick bonded to steel shells.
Babbitt have excellent conformability and embeddability. Tin-base Babbitt have better corrosion resistance and can be easily bonded to steel shells. High cost and shortage of tin are their main limitations. Babbitt’s, whether lead-base or tin-base, are inherently weak and their strength decreases rapidly with increasing temperature.
14. Bearing companies:
Here is the list of some top companies to refer their catalogue for bearing selection.
Basics questions asked in Interview.
- What are functions of bearing?
- What is radial bearing?
- What is thrust bearing?
- What is sliding contact bearing?
- What is rolling contact bearing?
- What are the applications of sliding contact bearing?
- What are the applications of rolling contact bearing?
- Name the various types of ball bearings?
- Name the various types of roller bearings?
- Why are taper roller bearings are used in pairs?
- Tell me basic bearing selection procedure?
Also you like to read:
1. Mechanical engineering interview questions and answers for freshers.
2. Top 30 HR Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers all Job.
3. Solid edge Interview questions and answers for freshers.
4. CATIA V5 Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers.

Such nice techniques
Very very informative post.
amazing bro thanks for sharing profitable knowledge
hi sir your post realy amazing and i got much information through your post and i realy thanks to that your post very helpfull for new learners…..
Thank you sir for this article.
For Certification online medical course. Visit our website: https://in.raaonlinecertify.com